Versions
- velero: v1.9.0
- gke: v1.25.6-gke.200
- velero helm charts: 2.30.1
- flux cd: 0.36.0
Import helm chart repository
- Create vmware-tanzu-helmrepo.yaml, add the following content and submit it to the git repository:
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta2
kind: HelmRepository
metadata:
name: vmware-tanzu
spec:
interval: 30m
url: <https://vmware-tanzu.github.io/helm-charts>
- Check if the helmrepo is working fine:
kubectl get helmrepository -A | grep vmware-tanzu. The output should be as follows:
flux-system vmware-tanzu <https://vmware-tanzu.github.io/helm-charts> 117d True stored artifact for revision 'eff1284a69fc7293ad2a4618c30d63ef6f486bd74ea3a8d3301866b899facdf6'
Install velero
- Create velero-release.yaml, add the following content and submit it to the git repository:
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2beta1
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: velero
spec:
chart:
spec:
chart: velero
sourceRef:
kind: HelmRepository
name: vmware-tanzu
namespace: flux-system
version: "2.30.1"
interval: 1h
maxHistory: 3
values:
backupsEnabled: false
snapshotsEnabled: true # Enable VolumeSnapshotLocation
deployRestic: true # If you need to use restic to back up PVC data, you need to enable this option
restic: # It is recommended to increase the default resource limits, otherwise backup may fail due to insufficient resources
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1000m
memory: 2Gi
limits:
cpu: 2000m
memory: 4Gi
configuration:
provider: gcp # Introduce GCP
features: "EnableUploadProgress" # Enable upload progress
initContainers: # Introduce GCP plugins
- name: velero-plugin-for-gcp
image: velero/velero-plugin-for-gcp:v1.4.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /target
name: plugins
credentials:
useSecret: false # We use workload identity
serviceAccount:
server:
create: true
name: velero
annotations: # Use GKE's workload identity and remember to give GCS permissions
iam.gke.io/gcp-service-account: <service-account-name>@<project-name>.iam.gserviceaccount.com
rbac:
create: true
clusterAdministrator: true
schedules: {}
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 500Mi
limits:
cpu: 1000m
memory: 1000Mi
Wait for fluxcd to automatically deploy velero. If the following pod appears, the installation is successful:
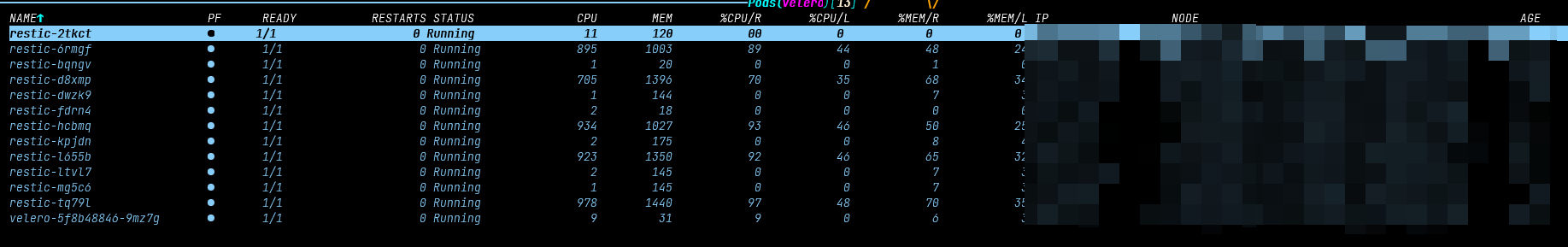
Check if the CRD is created successfully:
kubectl get crd | grep velero. The output should be as follows: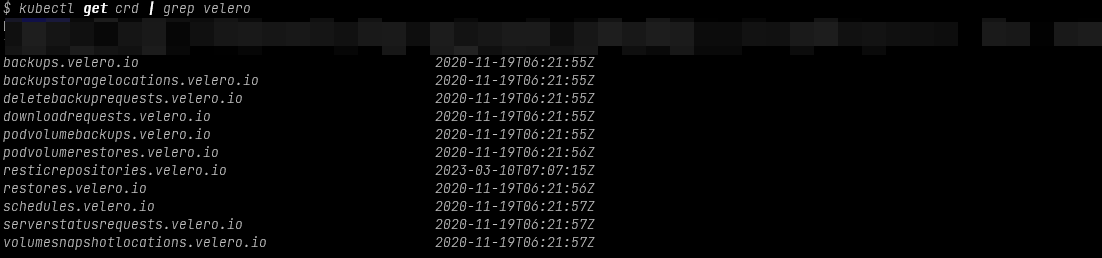
Test backup
- Create a test pod and PVC and deploy:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: test-backup-volume-claim
namespace: staging
spec:
storageClassName: test-backup-storage-class
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-backup
namespace: staging
labels:
app: test-backup
spec:
containers:
- name: test-backup
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/var/www/html"
name: mypd
volumes:
- name: mypd
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: test-backup-volume-claim
- Write file data to
/var/www/htmlin the pod. - Create a backup plan:
apiVersion: velero.io/v1
kind: Schedule
metadata:
name: test-backup
namespace: velero
spec:
schedule: "0 14 * * 1"
template:
includedNamespaces:
- staging
volumeSnapshotLocations: [default]
storageLocation: default
includedResources:
- "*"
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app: test-backup
snapshotVolumes: true
defaultVolumesToRestic: true
ttl: 168h # 7 days
- Create a backup based on the schedule:
velero backup create --from-schedule test-backup. The return value is as follows:
Creating backup from schedule, all other filters are ignored.
Backup request "test-backup-20230314070438" submitted successfully.
Run `velero backup describe test-backup-20230314070438` or `velero backup logs test-backup-20230314070438` for more details.
- Use
velero backup describe test-backup-20230314070438 --detailsto check the task status.

